Errore nel formato dell'e-mail
emailCannotEmpty
emailDoesExist
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd


Understanding NTC Thermistors: A Guide to their Working Principle and Buying Tips
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors widely used in various applications. In this article, we will explore how NTC thermistor it works and provide essential buying tips for those considering purchasing them.
1. What is an NTC Thermistor?
NTC thermistors are passive electronic components whose electrical resistance decreases as the temperature rises. They are typically made of metal oxides and exhibit a nonlinear resistance-temperature relationship. This unique characteristic makes them exceptionally useful in temperature sensing and control applications.
2. Working Principle of NTC Thermistors:
NTC thermistors operate based on the behavior of the semiconductor material used in their construction. The material's resistance decreases with increasing temperature due to the movement of charge carriers within the crystal lattice.
3. Temperature-Resistance Relationship:
The resistance of an NTC thermistor is inversely proportional to the temperature. As the temperature increases, the number of charge carriers also increases, resulting in a lower resistive path for the electric current.
4. Steinhart-Hart Equation:
To establish a precise relationship between resistance and temperature, the Steinhart-Hart equation is commonly used. This equation mathematically describes the nonlinearity of the NTC thermistor and provides accurate temperature calculations based on its resistance.
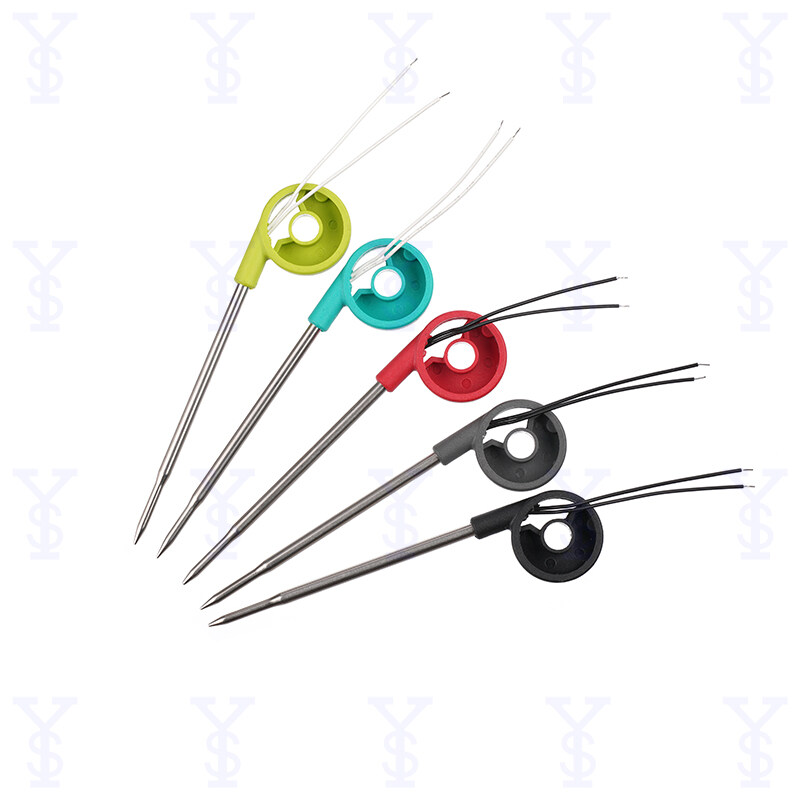
5. Applications of NTC Thermistors:
NTC thermistors find wide-ranging applications, including:
A. Temperature Sensing:
NTC thermistors are commonly used as temperature sensors in household appliances, industrial processes, and environmental monitoring systems. They are highly accurate and provide fast response times.
B. Temperature Compensation:
In applications where maintaining stable electrical characteristics is essential for proper device operation, such as in power supply circuits and analog-to-digital converters, NTC thermistors are used for temperature compensation.
C. Protection:
NTC thermistors are employed in various electrical and electronic devices to protect against overheating. When the temperature exceeds the specified threshold, they trigger a protective action such as shutting down the system or activating an alarm.
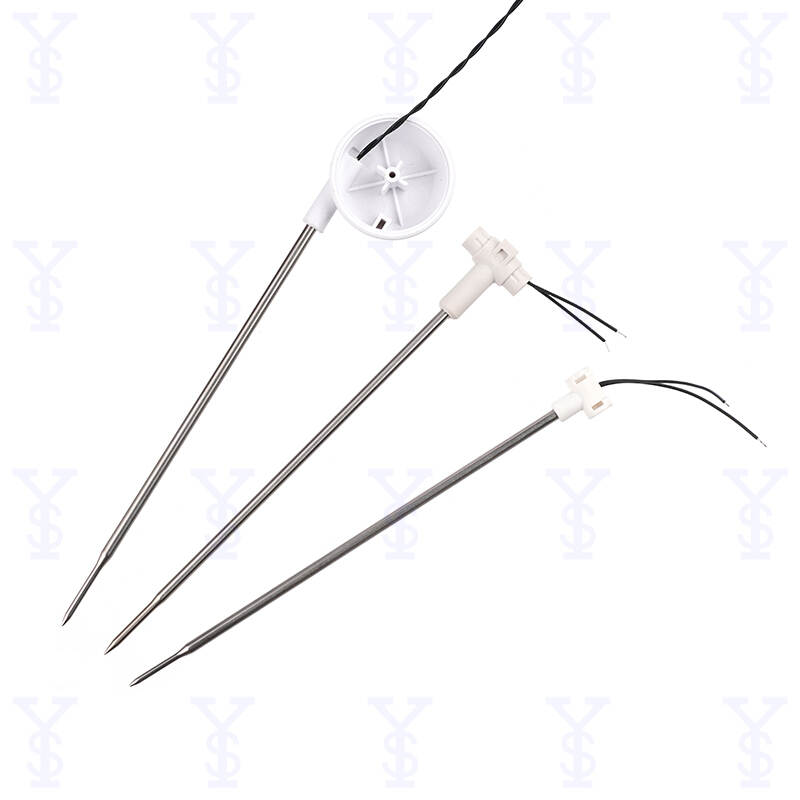
6. Buying Tips for NTC Thermistors:
When buying NTC thermistors, consider the following factors:
A. Resistance and Tolerance:
Choose an NTC thermistor with the appropriate resistance value for your intended application. Ensure the specified tolerance is acceptable for your requirements.
B. Temperature Range:
Check the thermistor's temperature range to ensure it covers the intended operating conditions. Consider both the minimum and maximum temperature limits.
C. Packaging:
Select the appropriate package type based on your application's needs, such as surface mount, through-hole, or leaded.
D. Operating Current and Power:
Verify that the NTC thermistor can handle the required operating current and power levels to prevent failure or damage.
E. Reliability and Quality:
Consider the reputation and reliability of the manufacturer or supplier. Look for certifications and quality standards compliance to ensure the thermistors are reliable and meet industry standards.

Conclusion
NTC thermistors are versatile temperature-sensitive resistors that can be used in a wide range of applications. Understanding their working principle and considering essential buying tips will help you select the appropriate thermistor for your needs. Whether for temperature sensing, compensation, or protection, NTC thermistors provide accurate measurements and are crucial components in various industries.